Spreads in Forex are the primary way traders are charged when opening and closing positions. Learn more about spreads and how they are calculated here.
What are Spreads in Forex?
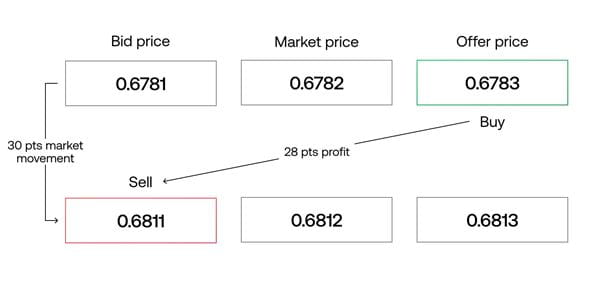
The spread in Forex is the difference between the price a broker quotes to buy a currency (ask) and the price a broker quotes to sell a currency (bid). Always buy slightly above market and sell slightly below market. This difference is called the bid/ask spread.
Spreads in Forex are the main cost of trading and should be considered a surrogate for commissions. As such, spreads may vary between brokers.
A high spread means that the difference between the selling and buying prices of a currency pair is large. A low spread, on the other hand, means that the difference between the selling and buying prices of a currency pair is small.
Check out our Beginner’s Guide to Forex Trading.
How are spreads calculated in Forex?
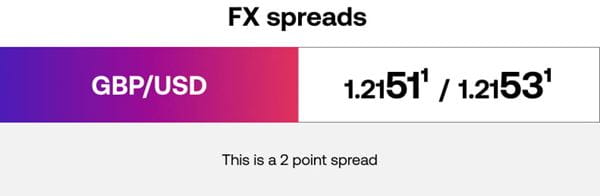
To calculate the spread in forex, you need to calculate the difference in pips between the buy and sell prices. For example, if you are trading GBP/USD at 1.2151 /1.2153, the spread will be calculated as 1.2153 – 1.2151 or 0.0002.
Spreads are usually measured in pips, the smallest unit of price movement for a currency pair. For most currency pairs, 1 pip is equivalent to 0.0001. The exception is the Japanese Yen, which is quoted only to two decimal places. So, in our GBP/USD example, 0.0002 would be a spread of 2 pips.
How spreads work in forex
Forex spreads vary slightly depending on what your broker offers. In general, there are two main types of spreads: fixed and floating.
- Fixed spreads are always the same regardless of volatility
- Variable spreads allow for varying levels of risk and can be tightened or loosened depending on volatility.
Fixed spreads are offered by providers who act as market makers themselves as counterparties to their clients’ trades, while variable spreads are more common among providers who pass on third-party pricing.
Fixed spreads are generally beneficial during periods of high volatility when spreads widen, while floating spreads may reduce costs in more stable market conditions.
Some forex traders prefer fixed spreads because they can be reasonably sure of the price they will pay and the costs they will incur. However, even fixed spreads can experience slippage. This happens when the market is moving rapidly and the price fluctuates between the level of the order and the price the broker is able to fill.
What Affects Forex Spread Costs?
The cost of spreads in forex depends on market conditions and the agreement with the broker, i.e. fixed or floating spreads.
Assuming variable spreads, transaction costs will be higher in volatile markets and lower in stable periods, taking into account the increased risk to the broker.
Volatility can be caused by many different factors, but forex is primarily influenced by the release of economic data and breaking news. This is why it is important to keep track of the dates on the economic calendar to see what future events may affect the currency pairs you are trading.
The selected FX pair also affects the cost of the spread. Emerging market and emerging country currency pairs typically have higher spreads than major currency pairs due to lower liquidity levels.
How do spreads affect Forex profits?
Spreads affect forex profits. Because you will always be buying above market and selling below market, there is an initial barrier that must be overcome before a trade can be profitable.
For example, if the EUR/USD market is trading at 1.0949 and the spread is 0.9, you would open a long position at 1.0950. This means that the underlying asset must rise 0.45 points above the current market price before a capital gain can occur on the trade.
What does raw spread in forex mean?
A raw spread forex account is a type of trading account that provides a direct link between traders and the market. In other words, there are no spreads added by the broker. The upside is that the cost per trade is lower and the profit potential can be slightly higher as there is no spread to cover before the position becomes profitable.
However, many raw spread accounts feature commissions instead of spread fees.
The problem is that by offering raw spreads, brokers are effectively passing on the transaction costs to individuals. This means that instead of spreads, you may have to pay higher fees for each trade execution.
Get low spreads with City Index
Trade over 84 global currency pairs with low transaction costs, including EUR/USD starting at just 0.7 points. To get started, just do the following:
- open a forex trading account – City Index allows you to choose between a standard trading account or an MT4 trading account
- Find Forex Pairs to Trade – Offering over 84 global currency pairs on our award-winning platform
- decide whether to go long or short – This depends on whether you think the base currency will strengthen or weaken relative to the market.
- strategize – Must develop a forex strategy for entering and exiting trades. This should include proper foreign exchange risk management.
- make a deal – Then monitor the market and close the position when the profit target or maximum loss is reached.
Learn more about how to trade forex
Alternatively, you can open a demo trading account if you are not yet ready to trade on the live market. You can access any of our currency pairs and take price positions using virtual funds instead of real cash.
Learn more about Forex trading with City Index here.
If you want to learn more about the forex market, take the City Index Academy’s Forex Trading Course for Beginners. We offer a wide range of different lessons that may be of interest to new FX traders, such as an overview of Forex trading, how to use technical analysis, how to participate in trading, and more.
See all courses for beginners

